Navigating Total Knee Replacement: Understanding Safety Concerns
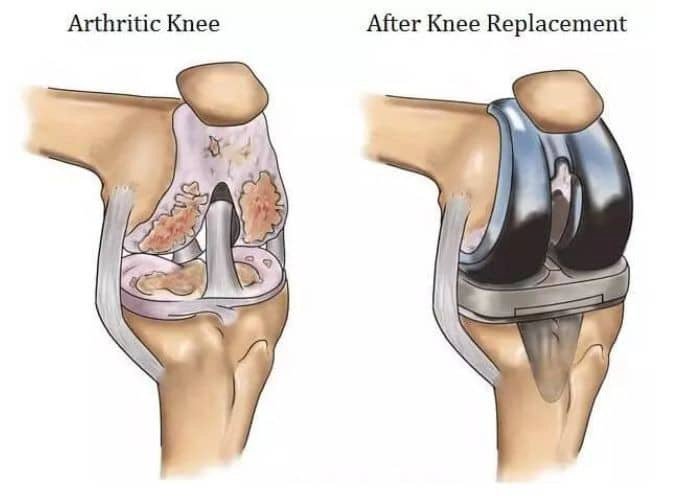
Total knee replacement (TKR), also known as total knee arthroplasty, is a surgical procedure that has become increasingly common for individuals suffering from severe knee pain and limited mobility due to conditions like osteoarthritis or rheumatoid arthritis. While it offers significant relief and improved function for many, questions about its safety often arise. Let's delve into some common concerns surrounding TKR and shed light on its safety profile.
Is TKR Dangerous?
First and foremost, it's essential to address the safety aspect of TKR. Like any surgical procedure, TKR carries certain risks, but advancements in medical technology and surgical techniques have significantly reduced these risks over the years. In fact, TKR is generally considered a safe and effective treatment for individuals who have exhausted non-surgical options without finding relief.
Potential Risks: While complications from TKR are rare, it's important to understand them to make informed decisions. According to studies, the overall complication rate for TKR is approximately 5% to 10%. These complications may include:
Infection: Although uncommon, occurring in less than 2% of cases, infection is one of the most serious complications associated with TKR. Strict adherence to sterile techniques in the operating room, antibiotic prophylaxis, and meticulous wound care help minimize this risk.
Blood clots: Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) and pulmonary embolism (PE) are potential risks following TKR, with an incidence rate ranging from 1% to 3%. To prevent blood clots, patients are often prescribed blood thinners and encouraged to mobilize early post-surgery.
Nerve or blood vessel damage: While rare, nerve or blood vessel damage can occur during surgery, with an incidence rate of less than 1%. Surgeons take precautions to minimize this risk, such as careful planning and precise surgical techniques.
Allergic reactions: Allergic reactions to materials used in the implant are rare, affecting less than 1% of patients. Pre-operative evaluations typically include screening for allergies to avoid potential complications.
Can TKR Cause Lymphedema?
Lymphedema is swelling caused by a buildup of lymph fluid. While TKR itself doesn't directly cause lymphedema, certain factors associated with surgery, such as decreased mobility during recovery, can potentially contribute to its development. However, with proper post-operative care, including physical therapy and gradual return to activity, the risk of lymphedema can be minimized.
Can Patients with Heart Conditions Have TKR?
Patients with heart conditions can undergo TKR, but careful evaluation and collaboration between orthopedic surgeons and cardiologists are essential. Studies indicate that individuals with pre-existing heart conditions may have a slightly higher risk of complications following TKR, including cardiovascular events. However, with proper medical management and perioperative care, the incidence of complications remains low. Close monitoring and individualized treatment plans help ensure the safety and success of TKR in patients with heart conditions.
Conclusion:
Total knee replacement is generally a safe and effective procedure for individuals suffering from debilitating knee pain and limited mobility. While risks exist, they are minimized through advancements in surgical techniques, pre-operative evaluations, and post-operative care protocols. Patients considering TKR should have open discussions with their healthcare providers to address any concerns and ensure they are well-informed about the procedure's safety and potential outcomes. With proper guidance and support, TKR can offer significant improvements in quality of life for those in need.